 Medically reviewed by Dr Rick Singh – Chief Medical Officer at NextCare. Dr. Rick Singh, Board Certified in Family Medicine and trained in Emergency Medicine, completed his residency at ProMedica Flower Hospital in Ohio. Joining NextCare in 2014, he advanced through leadership roles before becoming Chief Medical Officer in February 2023.
Medically reviewed by Dr Rick Singh – Chief Medical Officer at NextCare. Dr. Rick Singh, Board Certified in Family Medicine and trained in Emergency Medicine, completed his residency at ProMedica Flower Hospital in Ohio. Joining NextCare in 2014, he advanced through leadership roles before becoming Chief Medical Officer in February 2023.
You wake up one morning and your shoulder feels stiff. You reach for your morning coffee, but ouch, a sharp pain shoots through your shoulder. Or maybe you’ve been feeling a nagging pain in your hip, especially after a long day of gardening. This pain might be bursitis, a common inflammatory condition. It’s time to understand what causes bursitis so we can prevent these painful flare-ups. You’ll learn exactly what causes bursitis and how to find lasting relief.
NextCare Urgent Care is one of the nation’s largest providers of urgent care and occupational medical services. With over 170 clinics across the country, NextCare offers immediate medical attention for non-life-threatening illnesses and injuries, including those related to joint pain and inflammation such as bursitis. If you’re experiencing symptoms that concern you, we are here to support your health and provide prompt care.
Understanding Bursitis: Why My Joints Hurt So Much
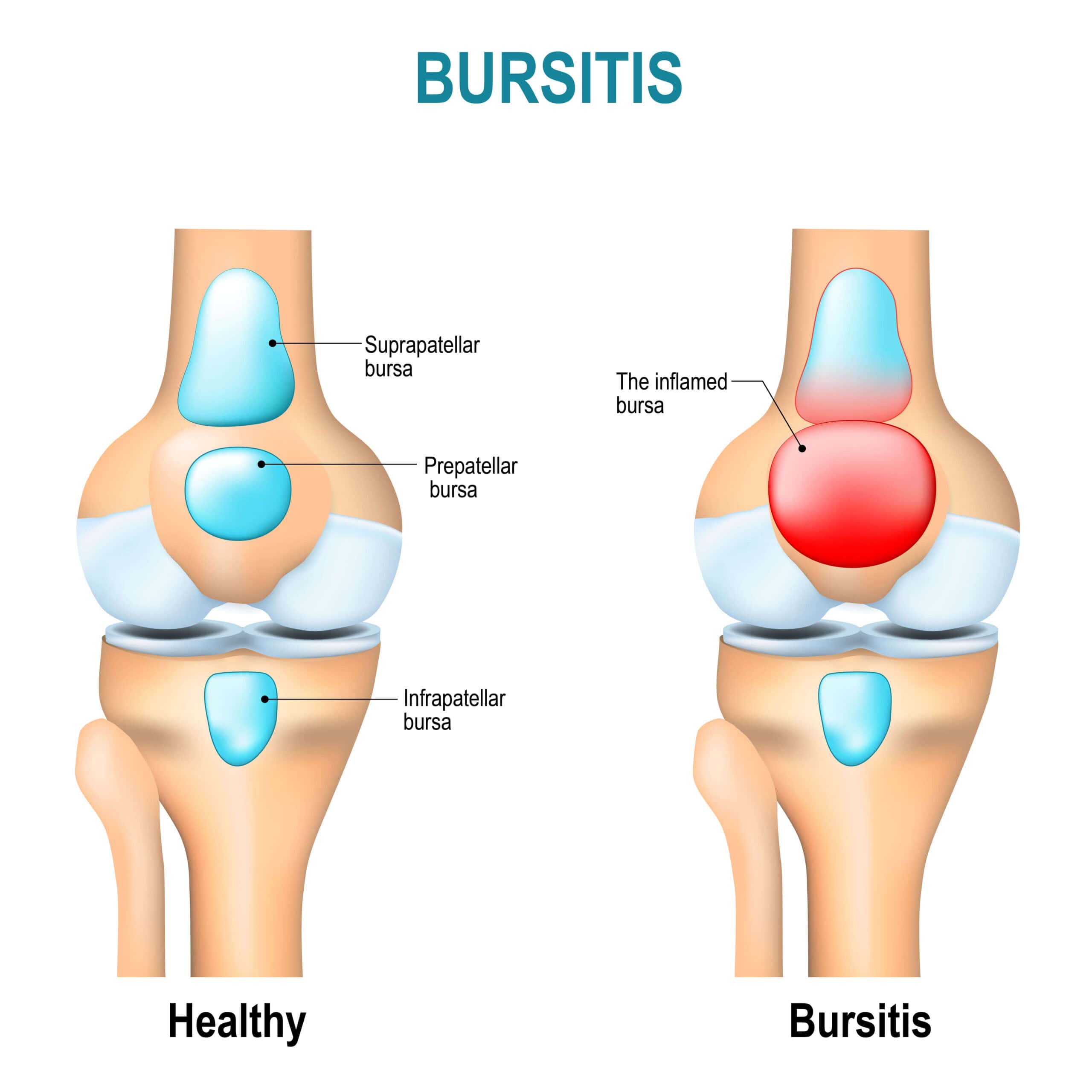
Imagine small fluid-filled sacs called bursae throughout your body, acting as cushions between your bones, muscles, and tendons. These helpful bursae reduce friction during movement.
Sometimes these bursae become irritated and inflamed – this is bursitis. Bursitis pain can develop suddenly or gradually over time, depending on what triggered it.
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is the painful swelling of a small, fluid-filled sac called a bursa. Think of bursae (the plural of bursa) as tiny cushions that protect spaces around your bones and other tissues. These sacs work like bubble wrap, offering protection to various structures throughout your body. They are strategically placed between bones and your muscles, tendons, and skin to reduce friction during movement.
Bursitis occurs when one of these bursae becomes irritated and swells. This inflammation can result in significant discomfort, with pain that may develop suddenly or gradually over time. The most common causes of bursitis include overuse or applying too much pressure to a bursa. Whether it’s from repetitive motions or prolonged pressure, understanding how bursitis develops is crucial for finding relief and preventing future episodes.
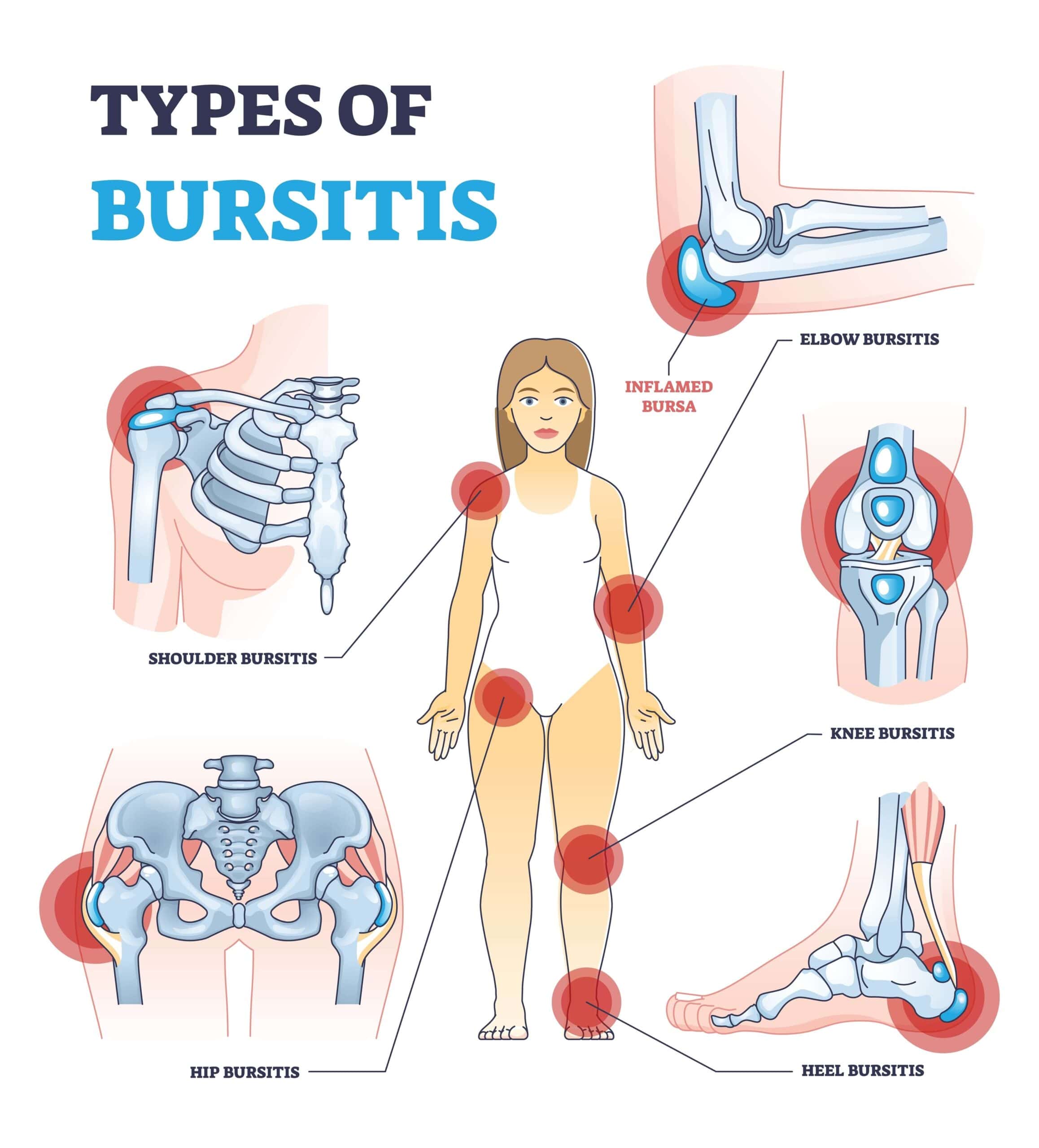
Different Types of Bursitis
With more than 150 bursae spread throughout your body, bursitis can strike in various locations, especially in joints frequently used for repetitive motions or areas under constant pressure. Here are some common types of bursitis, each affecting different parts of the body:
- ⊕ Shoulders (Subacromial Bursitis): This type of bursitis affects the bursa located under the acromion, part of the shoulder blade. It can cause pain, particularly when lifting the arm.
- ⊕ Elbows (Olecranon Bursitis): Often referred to as miner’s elbow or barfly’s elbow, this form of bursitis occurs at the tip of the elbow, leading to noticeable swelling and tenderness.
- ⊕ Knees (Prepatellar Bursitis): Also known as housemaid’s knee, this type occurs over the kneecap, making kneeling and other movements particularly uncomfortable.
- ⊕ Feet (Heel Bursitis): Bursitis near the heel or around the big toe or ball of the foot can make walking painful and difficult.
- ⊕ Hips (Trochanteric Bursitis): This type affects the outer part of the upper thigh, leading to sharp pain that can radiate down the leg, especially when lying on the affected side.
- ⊕ Buttocks (Ischial Bursitis): Sometimes called weaver’s bottom, this bursitis occurs in the buttocks and can cause discomfort when sitting.
While healthcare providers might refer to these types of bursitis by specific names, they all stem from the same issue: swelling in and around a bursa. Recognizing the type of bursitis you have is the first step in addressing the pain and taking steps toward effective treatment and prevention.
Unmasking the Culprit: What Causes Bursitis Anyway?
Bursitis usually stems from everyday activities, especially those involving repetitive movements or sustained pressure on certain joints. Let’s explore some common causes.
1. Repetitive Motions: When Everyday Activities Become Bursitis Triggers
Repetitive motions at work or from our hobbies can contribute to bursitis. Jobs involving repetitive movements, such as carpentry, gardening, and painting can lead to bursitis. Certain hobbies, especially those that require repetitive hand motions, are also suspect.
For example, playing a musical instrument increases your risk for developing bursitis. Anyone can experience bursitis, but people who do physical or manual labor, athletes, and musicians may be at a higher risk.
2. Prolonged Pressure on Joints: How Our Habits May Be Setting Us Up for Bursitis
Spending long periods in positions that put pressure on specific joints can cause bursitis. For example, kneeling for extended durations (think gardening or laying carpet) can lead to bursitis, especially as we age and our tendons become less elastic.
Even something as simple as poor posture can put excess stress on our joints over time and make us vulnerable to bursitis. Maintaining good posture can go a long way in preventing those bursae from protesting.
3. Injuries: Sometimes a Sudden Impact is the Culprit Behind Bursitis
A sudden impact or injury, like falling on your knee or bumping your elbow, can lead to bursitis. While these injuries can happen during sports, they can also occur during everyday activities. Even bumping your elbow on a hard surface can irritate those bursae.
4. Infections: Did You Know Bacteria Can Trigger Bursitis?
An infection can sometimes be the root cause of bursitis. This occurs when bacteria enter a bursa, typically after an injury or cut. That’s why it’s important to treat even minor wounds properly.
Your doctor can check for any signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, fever, or if the bursitis symptoms are persistent. Bacterial infections that lead to bursitis can often be treated with antibiotics prescribed by your healthcare provider.
5. Underlying Health Conditions: Pre-Existing Conditions That Can Make You Susceptible to Bursitis
Certain health conditions can increase your chances of experiencing bursitis. These conditions create inflammation throughout the body, including in the joints, making them breeding grounds for those bursa sacs to flare up.
Medical conditions, such as arthritis, gout, and diabetes, can increase a person’s risk of developing bursitis.
So Now That I Know What Causes Bursitis, What Does It Feel Like? Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
So how do we know when those little bursa sacs are acting up, causing us grief? Bursitis usually causes localized pain, especially during movement or when applying pressure to the affected area.
While any bursa in the body can be affected, bursitis commonly affects the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and heel. The painful swelling is often described as achy or stiff, and it seems to worsen when you try to move the joint.
| Type of Bursitis | Common Location | Telltale Symptoms You May Be Experiencing |
|---|---|---|
| Shoulder Bursitis | In the shoulder joint (often involves the subacromial bursa) | A deep, achy pain that intensifies when lifting the arm. It’s often accompanied by tenderness around the shoulder, pain at night, and restricted range of motion. |
| Elbow Bursitis (Olecranon Bursitis) | At the pointy part of the elbow | A noticeable bump and swelling over the elbow. It’s typically quite tender to touch. Moving your elbow, particularly bending it, may cause discomfort, and you might also have limited movement in the joint. |
| Hip Bursitis (Trochanteric Bursitis) | Over the outer portion of the upper thigh | Sharp hip pain, especially on the outer part of the hip, which can radiate down the thigh. The area might be tender to touch and often worsens when you lie on it. Walking, climbing stairs, and standing for long durations often trigger pain. |
| Knee Bursitis (Prepatellar Bursitis) | Over the kneecap | Swelling, pain, tenderness, and warmth over the kneecap. It can make it difficult to straighten or bend your knee or walk comfortably. |
| Heel Bursitis (Achilles Bursitis) | At the back of the heel, where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel bone. | Pain, swelling, and tenderness at the back of the heel. This pain tends to worsen with activity, especially running or jumping. You may also experience pain when you first wake up in the morning or after a period of |
Diagnosis and Tests: How is Bursitis Diagnosed?
When that persistent pain just won’t go away, it’s time to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. Diagnosing bursitis typically starts with a thorough physical exam. Your provider will ask about your symptoms, paying close attention to when the pain started and what you were doing at the time. This information is crucial, especially if your job or hobbies involve repetitive motions, which are common culprits behind bursitis.
During the exam, your provider will carefully examine the affected area, checking for signs of swelling, tenderness, and warmth. They’ll also assess your range of motion to see how the pain is affecting your ability to move. This hands-on approach helps your provider get a clearer picture of what’s going on beneath the surface.
NextCare Urgent Care offers convenient and timely access to diagnostics, including physical exams and tests necessary to diagnose bursitis. If you suspect bursitis, seeking an evaluation at one of our clinics can help you get on the right path to treatment.
What Tests Are Done to Diagnose Bursitis?
In addition to the physical exam, your healthcare provider might recommend a few tests to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. These tests can provide valuable insights into the extent of inflammation and whether an infection is involved.
- ⊕ X-rays: Although X-rays can’t directly show bursitis, they help rule out other conditions like fractures or arthritis that might be causing your symptoms.
- ⊕ Ultrasound or MRI: These imaging tests are more precise in detecting swollen bursae. Ultrasound is particularly useful for visualizing the soft tissues around your joints, while MRI offers a detailed view, especially if your provider suspects a more complex issue.
- ⊕ Blood Tests: If there’s a concern about infection, a blood test might be ordered. This can help identify any underlying infections that could be causing or worsening your bursitis.
- ⊕ Aspiration: In cases where infection is suspected, your provider might perform an aspiration. This involves using a needle to withdraw fluid from the swollen bursa. The fluid is then analyzed to check for infection or other underlying conditions.
Getting the right diagnosis is the first step toward effective treatment, allowing you to address the problem head-on and find the relief you need.
Effective Bursitis Treatment Options
Okay, time for the good news. In most cases, bursitis clears up with a little TLC. But this isn’t a “grin and bear it” situation. Recognizing the symptoms early and pursuing the right treatment is key to relieving pain.
So, how do you tame the inflammation and reclaim your pain-free life?
1. Conservative Care: At-Home Remedies
Good old-fashioned home care often does the trick for mild bursitis, especially in the early stages. This was my go-to when I first felt discomfort in my shoulder.
| Home Remedies | What to Do |
|---|---|
| Rest | Avoid activities that trigger the pain. Think of it like hitting the pause button on aggravating movements. This gives those inflamed bursae time to chill out and recover. |
| Ice and Heat Therapy | Apply ice packs for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day. This can reduce swelling and numb the pain. Later, switch to heat therapy, like a warm bath or heating pad, to relax muscles and improve blood flow. |
| Over-the-Counter Relief | Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or naproxen sodium, are your allies in fighting inflammation. Always stick to recommended dosages and consult your doctor if you have any concerns about interactions with other medications. |
Sometimes, adding extra cushioning with supportive gear helps, especially for hip or knee bursitis. And don’t underestimate the power of an anti-inflammatory diet.
2. Seeking Expert Guidance: When to Call the Doctor
While home remedies often work wonders, sometimes, bursitis needs a bit more than just rest and ice packs. If your pain is intense, lingers for more than two weeks, or is accompanied by fever, it’s time to call your healthcare provider. Redness around the affected area is another sign you may need medical intervention.
3. Medical Interventions: Treating More Severe Cases
Depending on the severity of your bursitis, your doctor might suggest additional interventions. Remember, bursitis treatment options vary depending on individual cases.
- ⊕ Physical Therapy: Physical therapy helps you regain strength, flexibility, and mobility. It is like rehab for your joints, with targeted exercises that help restore proper movement. It can also reduce the risk of future flare-ups.
- ⊕ Medications: If your doctor suspects your bursitis might have an infection brewing, they may prescribe antibiotics to tackle the source of inflammation.
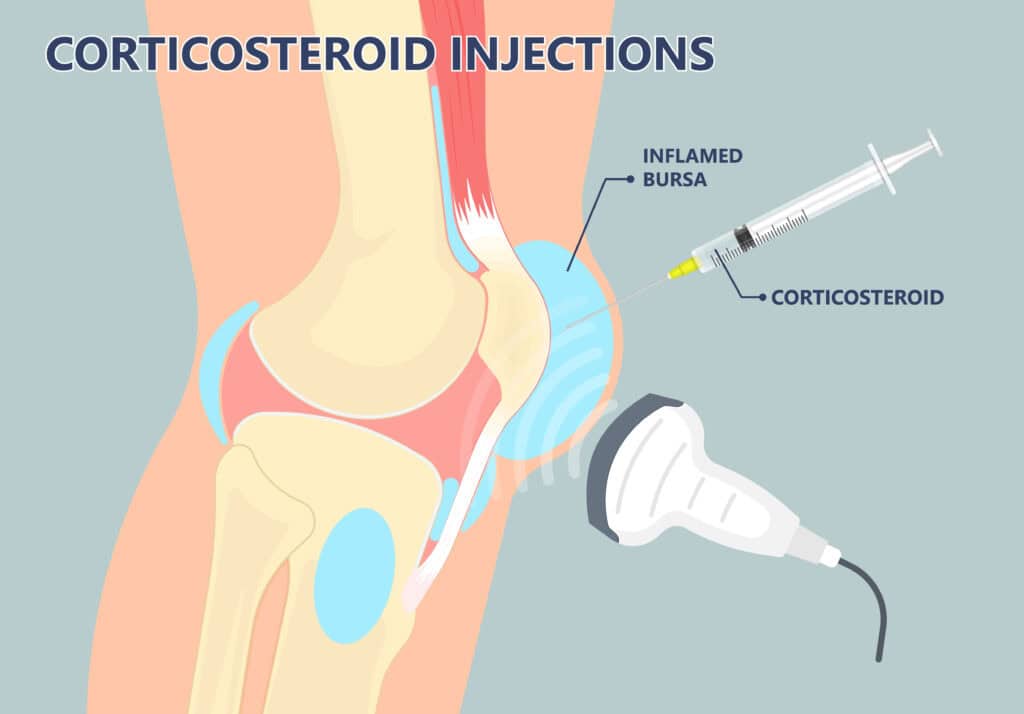
- ⊕ Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections directly into the affected bursa help reduce inflammation quickly and effectively. This provided significant relief for me when my shoulder bursitis was at its worst.
- ⊕ Aspiration: If a significant buildup of fluid is contributing to the pain, aspiration may be necessary. Using a needle, the doctor removes excess fluid from the bursa.
- ⊕ Surgery: The last resort for bursitis. This might involve surgically draining or removing the bursa altogether. But don’t fret; surgery is usually reserved for those rare cases that stubbornly refuse to respond to other treatment methods.
Preventing Bursitis: Keeping Pain at Bay
Who wants to endure the misery of bursitis? Instead of treating it after it flares up, why not outsmart it altogether? While there are no ironclad guarantees, adopting healthy habits can go a long way in minimizing the risks.
If you’re prone to bursitis, talk to your doctor about exercises that can strengthen muscles. Being overweight or obese is also a risk factor for bursitis, so talk to your doctor about a weight loss plan if that applies to you.
Conclusion
We’ve explored what causes bursitis and how to approach this common condition.
Remember, whether it’s a persistent ache from repetitive motions or a sudden pain in your shoulder, it’s important to address the root cause to experience relief. Early identification, proactive measures, and a bit of mindful movement can be powerful tools in our quest for lasting relief and a pain-free, fulfilling life.
FAQs
One frequent trigger is performing the same movements repeatedly, especially at work. Another common trigger is prolonged kneeling, such as when laying tiles or gardening.
Rest. Giving the affected area a break and avoiding activities that aggravate it often allows it to resolve. Seeking guidance from a healthcare provider is essential, especially if you’re dealing with severe or persistent symptoms, redness, swelling, warmth, or if you’ve had an injury that punctured your skin.
Continuing activities that aggravate the affected joint will often intensify bursitis. It’s essential to avoid repetitive motions and excessive pressure on the already irritated bursae to support healing.
Avoid movements or activities that put direct stress on the affected area. For example, if you have elbow bursitis, you may want to refrain from playing tennis or painting.
If only there was a magic wand for this. The healing process varies from person to person, but the fastest route involves a combination methods. Early intervention with rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain relief, plus following your doctor’s recommendations, is key.
Ignoring it will only prolong your misery.
While exciting advancements are always happening in medicine, no single “new” wonder treatment for bursitis exists. Research continually explores more effective treatments, but they usually build upon existing therapies, such as targeted drug delivery or minimally invasive procedures.
This depends on the underlying cause and individual factors. Your doctor can help determine the best medication for your specific type of bursitis. Never self-medicate without consulting a medical professional. They can consider potential drug interactions and other medical conditions.
The first line usually involves the conservative measures we talked about earlier: rest, ice, compression, and elevation (also known as the RICE protocol), along with over-the-counter pain relievers. These initial steps address inflammation and give your body a chance to heal.
If conservative approaches don’t cut it, your doctor might then consider other treatment options.
Treatment options are tailored to the patient’s current condition and the examples are to be used as possible treatment options. The actual treatment will be determined after an assessment performed by a medical professional. Additionally, procedures are recommended only after a comprehensive evaluation and a thoughtful determination of the most appropriate treatment options.
