Medically reviewed by Dr Rick Singh – Chief Medical Officer at NextCare. Dr. Rick Singh, Board Certified in Family Medicine and trained in Emergency Medicine, completed his residency at ProMedica Flower Hospital in Ohio. Joining NextCare in 2014, he advanced through leadership roles before becoming Chief Medical Officer in February 2023.
Medically reviewed by Dr Rick Singh – Chief Medical Officer at NextCare. Dr. Rick Singh, Board Certified in Family Medicine and trained in Emergency Medicine, completed his residency at ProMedica Flower Hospital in Ohio. Joining NextCare in 2014, he advanced through leadership roles before becoming Chief Medical Officer in February 2023. Pneumonia is a significant respiratory infection that can arise from bacterial, viral, or fungal causes. This article breaks down the different types, risk factors like existing health conditions and lifestyle habits, and the critical steps for prevention. We’ll cover the diagnostic methods healthcare professionals use, including chest X-rays and blood tests, and discuss effective treatments ranging from antibiotics to oxygen therapy.
Additionally, preventive strategies such as vaccinations and adopting healthier habits like proper diet and regular exercise are highlighted to help reduce your risk.
NextCare is one of the nation’s largest providers of urgent care and occupational medical services. With 170+ clinics in Arizona, Colorado, Kansas, Michigan, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Texas, Virginia and Wyoming, we offer exceptional, affordable care to patients across the country.
What is Pneumonia?
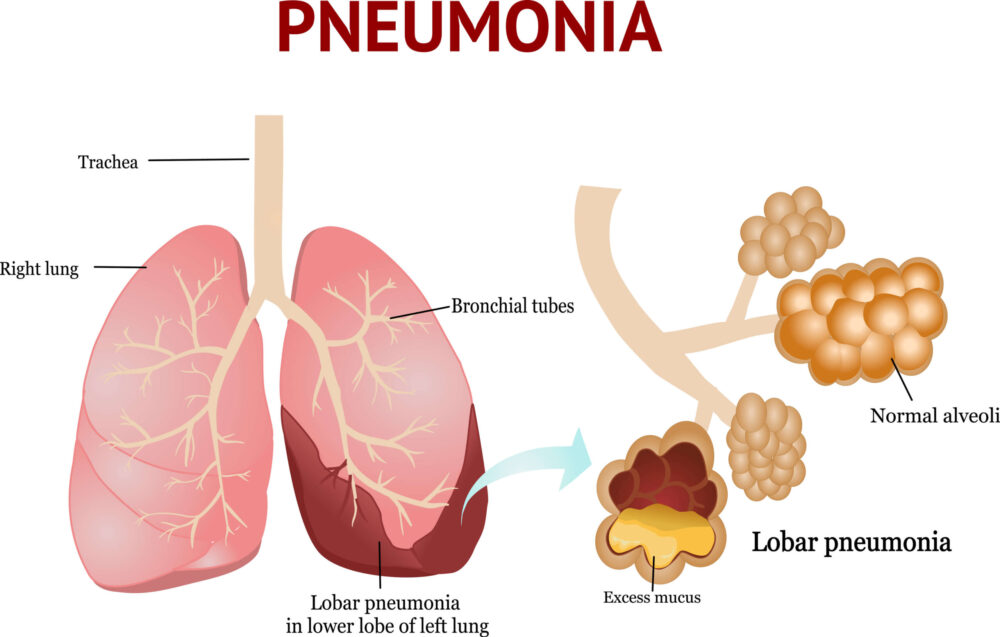
Pneumonia is a respiratory condition characterized by inflammation of the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs, known as alveoli, may fill with fluid or pus, leading to various respiratory symptoms. It can be caused by a variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and can range in seriousness from mild to life-threatening.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Pneumonia
Understanding the signs and symptoms of pneumonia is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. This lung infection, while common, can present a range of symptoms that vary in intensity depending on the individual’s health status and the type of pneumonia they have.
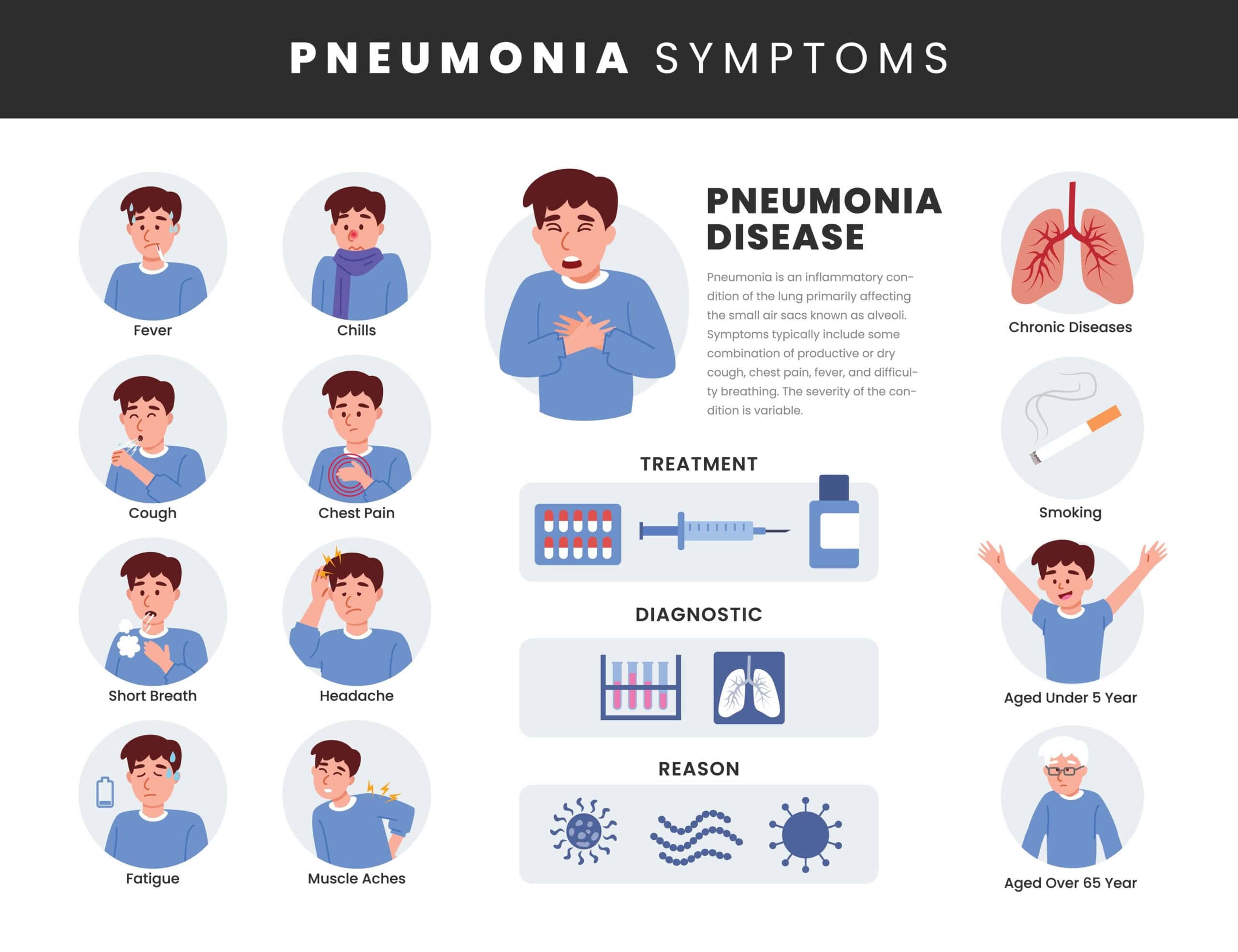
Common Symptoms of Pneumonia:
- ⊕ Cough: This may be a persistent cough that produces phlegm which can be clear, yellow, green, or even bloody.
- ⊕ Fever: You may experience a high fever along with sweating and shivering chills, indicating your body’s response to the infection.
- ⊕ Breathing Difficulties: Shortness of breath, especially with exertion, is a common symptom. You may feel like you can’t get enough air, which can be distressing and may worsen without treatment.
- ⊕ Chest Pain: Sharp or stabbing chest pain that worsens when you breathe deeply or cough, highlighting the inflammation or infection in the lung tissue.
- ⊕ Fatigue and Weakness: Pneumonia can leave you feeling severely fatigued and weak, making even daily activities challenging.
Additional Symptoms to Watch For:
- ⊕ Nausea and Vomiting: Especially in younger children, these symptoms can accompany pneumonia, complicating their nutrition and hydration.
- ⊕ Confusion: Older adults may exhibit signs of confusion or changes in mental awareness if they have pneumonia, which is a symptom that should prompt immediate medical attention.
By staying alert to these symptoms, individuals can seek early medical intervention, which is key to a swift recovery. If you or someone you know exhibits these signs, it is advised to consult with healthcare professionals promptly to ensure proper care and treatment.
Remember, early detection and treatment not only improve recovery rates but also help prevent complications associated with pneumonia.
Causes of Pneumonia and How It’s Acquired
Pathogens responsible for pneumonia can be contracted through inhalation, aspiration, or spread through the bloodstream. It is essential to understand both the pathogens that cause pneumonia and the contexts in which it is acquired—be it within the community, a hospital, or through mechanical ventilation.
Here’s a breakdown of the types of pneumonia based on both the causative agent and the acquisition context:
Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
This is the most common type and occurs outside of healthcare settings. The causes vary:
Bacterial pneumonia
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia. Other bacteria, including Haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus, may also be responsible for this type of infection. Bacterial pneumonia often occurs after an upper respiratory tract infection like cold or flu when your immune system is weakened.
Viral pneumonia
Viral infections like influenza (flu), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are known causes of viral pneumonia. Viral pneumonias tend to be less severe than bacterial ones but still require proper medical attention.
Fungal pneumonia
- ⊕ Pneumocystis jirovecii: A fungus causing a form of fungal pneumonia called Pneumocystis jirovecii (formerly Pneumocystis carinii) which primarily affects people with compromised immune systems due to conditions like HIV/AIDS.
- ⊕ Cryptococcus neoformans: Found in soil contaminated with bird droppings; it poses a risk mainly for individuals with weak immunity such as organ transplant recipients or those undergoing chemotherapy.
- ⊕ Aspergillus: A common mold that can cause pneumonia in people with lung diseases, weakened immune systems, or who have had a recent organ transplant.
In general, fungal pneumonias are less common than bacterial and viral ones but can be particularly dangerous for individuals with compromised immunity. It’s essential to identify the specific cause of pneumonia so that appropriate treatment measures can be taken.
Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) and Healthcare-Associated Pneumonia (HCAP)
These types occur within medical settings and often involve more resistant bacteria such as MRSA, which are challenging to treat.
Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP)
Affects individuals using mechanical ventilators, often in intensive care units, and can involve a variety of pathogens, including drug-resistant bacteria.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Results from inhaling food, liquid, vomit, or saliva into the lungs, often leading to a different treatment approach compared to other types of pneumonia.
Risk Factors for Developing Pneumonia
Anybody can contract pneumonia, yet certain individuals are more susceptible because of existing medical issues or way of life elements.
Pre-existing Health Conditions
Individuals with chronic lung diseases like cystic fibrosis or COPD have a higher risk of developing pneumonia, as do those with weakened immune systems due to conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS. Young children under 2 and adults over 65 are also more susceptible.
Smoking and Alcohol Use
Smoking damages the lungs’ natural defenses against infections, making smokers more likely to contract pneumonia. Excessive alcohol consumption also weakens the immune system’s ability to fight off bacteria and viruses responsible for causing pneumonia. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake can significantly reduce your chances of getting this potentially dangerous infection.
- ⊕ Action step: If you’re a smoker looking for support in quitting, visit Smokefree.gov for resources and assistance.
- ⊕ Action step: For tips on reducing alcohol consumption, check out the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism’s guide.
Additional At-Risk Groups
- ⊕ Pregnant Women: Changes during pregnancy can affect lung capacity and immune function, making pregnant women more susceptible to pneumonia.
- ⊕ People with Occupational Hazards: Those exposed to toxic chemicals or pollutants regularly may have increased risk due to lung irritation.
Diagnosing Pneumonia Accurately
Physicians utilize chest X-rays, blood work, and physical examinations to diagnose pneumonia and assess its degree of seriousness.
Chest X-rays
A chest X-ray is the first step in diagnosing pneumonia, revealing inflammation or fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Blood tests
Blood tests, including a complete blood count (CBC) and specific blood cultures, can identify an active infection and the causative organism.
Physical examination
- ⊕ Fever: Doctors check for fever, a common symptom of pneumonia.
- ⊕ Difficulty breathing: Shortness of breath or rapid breathing due to lung inflammation.
- ⊕ Cough: A persistent cough producing mucus or phlegm is another symptom of pneumonia.
- ⊕ Auscultation: Abnormal lung sounds detected during auscultation, such as crackles or wheezing, may indicate pneumonia.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for timely recovery, and these diagnostic tools help doctors create an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia Patients
Don’t let pneumonia get you down – fight back with these treatment options.
Antibiotics
If bacteria are the culprit, antibiotics are the answer – just make sure to finish the entire course.
Oxygen therapy
Breathe easy with supplemental oxygen delivered through a mask or nasal cannula.
Intravenous fluids
Stay hydrated and balanced with IV fluids during recovery.
Over-the-counter medications
- ⊕ Fever reducers: Knock out fever and body aches with acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
- ⊕ Cough suppressants: Get temporary relief from coughing, but check with your doctor first.
- ⊕ Decongestants: Clear up congestion, but use with caution if you have high blood pressure or heart problems.
Remember to seek medical care promptly if you suspect pneumonia – visit NextCare Urgent Care for diagnosis and tailored pneumonia treatment options.
Prevent Pneumonia with These Simple Steps
Lower your odds of getting pneumonia by being immunized, staying healthy, observing proper cleanliness habits, and consulting a doctor when necessary.
Vaccination
Get vaccinated with Pneumovax 23® and Prevnar 13® to protect against pneumonia-causing bacteria.
Healthy Habits
- ⊕ Eat well: A balanced diet with fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins strengthens your immune system.
- ⊕ Exercise: Regular physical activity improves lung function and boosts immunity.
- ⊕ Sleep: Get enough rest to support optimal immune function.
Good Hygiene
Wash hands frequently, use hand sanitizer, cover mouth when coughing or sneezing, and avoid close contact with sick individuals.
Seek Medical Care
Don’t ignore symptoms like high fever, cough, or difficulty breathing. Seek medical attention promptly for early diagnosis and treatment.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Pneumonia
Stay healthy and prevent pneumonia by adopting these simple lifestyle habits.
Quit Smoking
Kick the habit to reduce your risk of pneumonia and improve lung function.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Boost your immune system with a healthy diet rich in fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Exercise Regularly
- ⊕ Aerobic exercise: Get your heart pumping with activities like brisk walking or swimming.
- ⊕ Muscle-strengthening exercises: Build muscle mass through resistance training to support overall physical health.
- ⊕ Flexibility exercises: Stretch regularly to promote good posture and mobility.
Advice from a medical practitioner should be sought prior to the commencement of any new exercise routine.
Wash Your Hands
Prevent the spread of germs by washing your hands regularly with soap and water.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can reduce your risk of pneumonia and promote overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a complex respiratory condition that requires timely and effective management to prevent serious health complications. Understanding the causes, recognizing early symptoms, and knowing the risk factors are crucial steps towards effective treatment and prevention.
Whether you suspect you have pneumonia or are seeking preventive care, NextCare’s experienced medical professionals are equipped with the knowledge and resources to assist you at every step. Visit your nearest NextCare location to get the quality treatment for pneumonia you deserve and breathe easier knowing you’re in good hands.
FAQs
A person can get pneumonia by inhaling bacteria, viruses, or fungi in the air or through close contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces.
- Bacterial infections: Such as Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Viral infections: Including the influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19.
- Fungal infections: Such as Pneumocystis jirovecii.
- Inhalation of foreign substances: Into the lungs can also cause pneumonia.
- Weakened immune system: Conditions like diabetes or HIV/AIDS can increase susceptibility.
Pneumonia can develop as a complication from other illnesses like colds or flu, but not all cases of sickness will result in this lung infection.
It’s important to take care of your immune system and practice good hygiene to reduce your risk of getting pneumonia.
Early signs of pneumonia may include:
- ⊕ Persistent cough, sometimes producing phlegm
- ⊕ Chest pain when breathing or coughing
- ⊕ Fever, sweating, and shivering chills
- ⊕ Shortness of breath during routine activities
- ⊕ Fatigue or feeling unusually weak
The progression of pneumonia can often be described in four stages:
- Congestion: Fluid accumulates in the lungs, causing infection.
- Red Hepatization: Lung tissue becomes firm and congested with blood cells.
- Gray Hepatization: Blood cells and fluids begin to disintegrate.
- Resolution: Lungs clear and restore normal function, though complete recovery might take time.
ndividuals with pneumonia should avoid foods that can increase mucus production or inflammation, such as:
- ⊕ Dairy products: Like milk and cheese, which might increase mucus in some people.
- ⊕ Refined sugars and processed foods: Can exacerbate inflammation.
- ⊕ Fried and fatty foods: Hard to digest and can strain the body during illness.
A diet rich in nutrients and antioxidants can support immune function and recovery:
- ⊕ Proteins: Such as lean meats, fish, and legumes.
- ⊕ Fruits and vegetables: Rich in vitamins and minerals.
- ⊕ Whole grains: Provide energy and fiber.
- ⊕ Hydration: Plenty of fluids, especially water, herbal teas, and broths.
Preventive measures include:
- ⊕ Vaccination: Especially against pneumococcal pneumonia and influenza.
- ⊕ Good hygiene practices: Regular hand washing, and covering mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- ⊕ Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking.