 Medically reviewed by Dr Rick Singh – Chief Medical Officer at NextCare. Dr. Rick Singh, Board Certified in Family Medicine and trained in Emergency Medicine, completed his residency at ProMedica Flower Hospital in Ohio. Joining NextCare in 2014, he advanced through leadership roles before becoming Chief Medical Officer in February 2023.
Medically reviewed by Dr Rick Singh – Chief Medical Officer at NextCare. Dr. Rick Singh, Board Certified in Family Medicine and trained in Emergency Medicine, completed his residency at ProMedica Flower Hospital in Ohio. Joining NextCare in 2014, he advanced through leadership roles before becoming Chief Medical Officer in February 2023. Yeast infections are incredibly common, affecting millions of people each year. If you’ve ever experienced the uncomfortable itching, burning, and unusual discharge associated with this condition, you’re not alone. In fact, research suggests 75% of females experience it during their lifetime. Let’s dive into the details of what causes these pesky infections and how to deal with them effectively.
NextCare Urgent Care provides immediate treatment for yeast infections. With 170+ clinics in Arizona, Colorado, Kansas, Michigan, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Texas, Virginia and Wyoming, we offer exceptional, affordable care to patients across the country.
Understanding Yeast Infections
At its core, a yeast infection is an overgrowth of a fungus called Candida. While small amounts of this fungus naturally live in our bodies, certain conditions can cause it to multiply rapidly, leading to an infection. The primary culprit is usually a species called Candida albicans.
These infections can occur in various parts of the body, but they’re most common in warm, moist areas like the vagina, mouth, and skin folds. Let’s break down the different types:
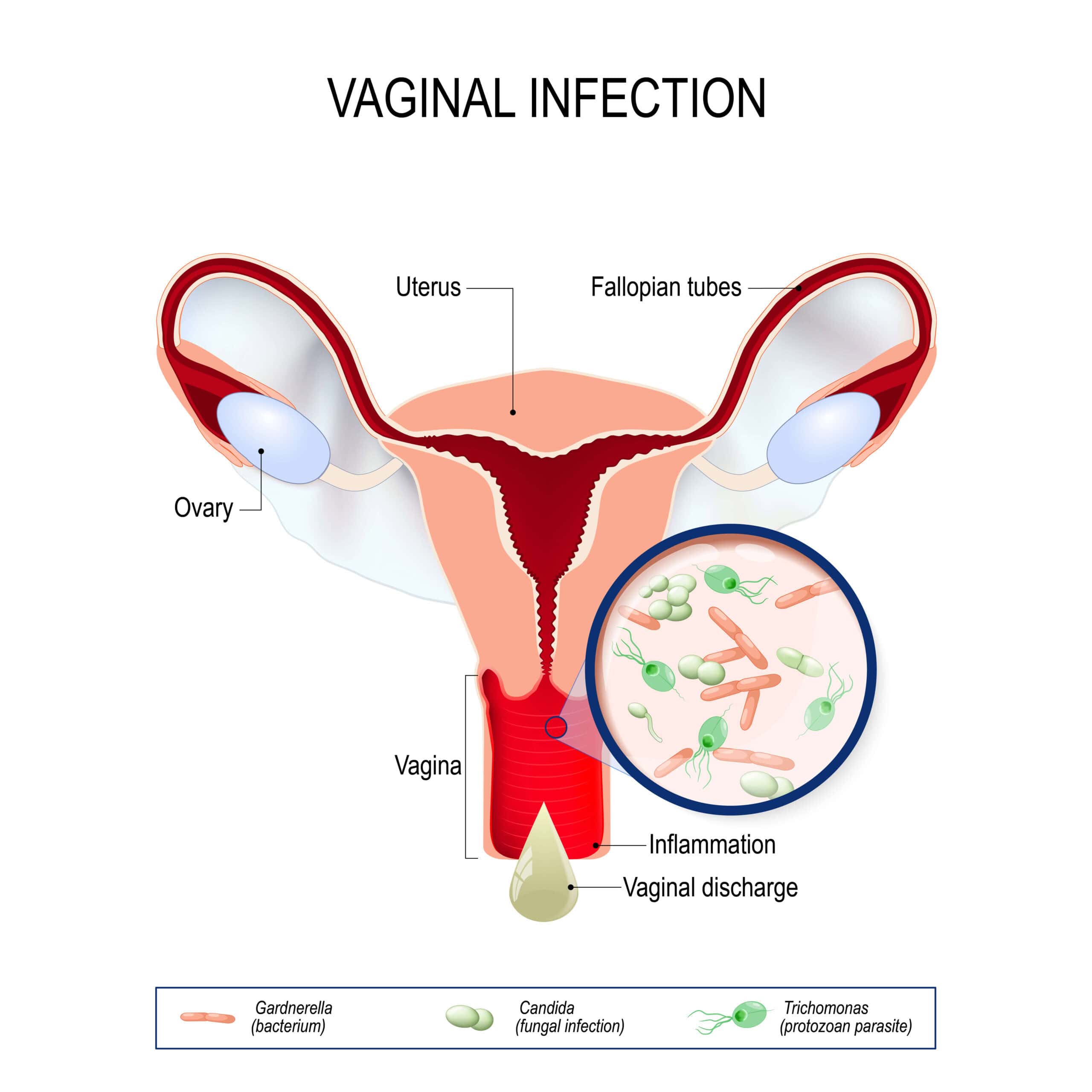
Vaginal Yeast Infections
The most well-known type, vaginal yeast infections, affect countless women worldwide. The common type of vaginal yeast infection can be characterized by vaginal candidiasis, which affects the vaginal opening. Symptoms often include:
- ⊕ Intense itching and irritation in the vagina and vulva
- ⊕ A burning sensation, especially during intercourse or urination
- ⊕ Redness and swelling of the vulva
- ⊕ Thick, white, odorless discharge with a cottage cheese-like appearance
Oral Thrush
When yeast overgrows in the mouth, it’s called oral thrush. This condition is a fungal infection that can cause:
- ⊕ White patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, or throat
- ⊕ Redness or soreness in the affected areas
- ⊕ Difficulty swallowing in severe cases
Skin Yeast Infections
Yeast can also infect the skin, particularly in warm, moist areas like armpits, groin, and under the breasts. Some people experience symptoms that may include:
- ⊕ Red, scaly, or raw skin
- ⊕ Itching and burning
- ⊕ Small red pustules or pimples
What Causes Yeast Infections?
Now that we understand what a yeast infection is, let’s explore why they occur. Several factors can disrupt the delicate balance of microorganisms in our bodies, leading to yeast overgrowth.
Antibiotics
While antibiotics are crucial for fighting bacterial infections, they can also kill off the beneficial bacteria that keep yeast in check. This is why many people experience yeast infections after a course of antibiotics. Antibiotics kill both good and bad bacteria, which can disrupt the balance.
Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in estrogen levels can create an environment more conducive to yeast growth. This is why yeast infections are more common during times when estrogen levels are in flux. Women experience these hormonal shifts in situations like:
- ⊕ Pregnancy
- ⊕ Menstruation
- ⊕ Menopause
- ⊕ When using hormonal contraceptives
Weakened Immune System
Conditions that suppress the immune system, such as HIV infection or cancer treatments, can make it harder for your body to keep yeast in check. When the immune system is compromised, it’s easier for yeast to grow unchecked.
Diabetes
High blood sugar levels can feed yeast, making infections more likely in people with uncontrolled diabetes. Uncontrolled diabetes can create an environment where yeast can thrive.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain habits can increase your risk of yeast infections. Many of these habits create warm, moist environments where yeast can flourish:
- ⊕ Wearing tight, non-breathable clothing
- ⊕ Staying in wet clothes (like swimsuits) for extended periods
- ⊕ Using scented feminine hygiene products
- ⊕ Douching, which disrupts the natural vaginal flora. Douching removes healthy bacteria that helps keep yeast in check.
Diagnosing Yeast Infections
If you suspect you have a yeast infection, it’s important to get a proper diagnosis. While over-the-counter antifungal treatments are available, many other conditions can mimic yeast infection symptoms. For example, bacterial vaginosis can be mistaken for a yeast infection.
Your urgent care doctor can diagnose yeast infections through several methods including:
- ⊕ A review of your symptoms and medical history
- ⊕ A physical examination
- ⊕ Laboratory tests, if necessary, to confirm the presence of yeast
Treatment Options
The good news is that yeast infections are highly treatable. The appropriate treatment may vary depending on the severity and location of the infection.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
For uncomplicated vaginal yeast infections, over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, or suppositories are often effective. These typically contain common antifungal agents such as:
- ⊕ Miconazole
- ⊕ Clotrimazole
- ⊕ Tioconazole
Prescription Medications
For more severe or recurrent yeast infections, your doctor may prescribe a different course of treatment. Treatment may include:
- ⊕ Oral antifungal medications like fluconazole (Diflucan)
- ⊕ Stronger topical antifungals
- ⊕ Long-term suppressive therapy for recurrent infections. Recurrent yeast infections are when a person experiences four or more yeast infections within a year.
Natural Remedies
While not as well-studied as conventional treatments, some people find relief with natural remedies. It is important to consult with a doctor before trying these alternative therapies, especially for pregnant women or those with underlying health conditions. Some common natural remedies include:
- ⊕ Probiotics to restore beneficial bacteria. The bacteria lactobacillus is a helpful bacteria that can be taken as a probiotic.
- ⊕ Tea tree oil (used externally)
- ⊕ Garlic, known for its antifungal properties
Always consult with a healthcare provider before trying natural remedies, especially if you’re pregnant or have other health conditions.
Preventing Yeast Infections
While it’s not always possible to prevent yeast infections entirely, you can reduce your risk by making some lifestyle changes. Here are some tips:
- ⊕ Wear breathable, cotton underwear
- ⊕ Avoid staying in wet clothes
- ⊕ Practice good hygiene, but avoid douching
- ⊕ Eat a balanced diet low in sugar and refined carbohydrates
- ⊕ Manage stress, which can affect your immune system
- ⊕ If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar under control
When to See a Doctor
While many yeast infections can be treated at home, certain situations warrant a visit to your healthcare provider. Seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- ⊕ If it’s your first suspected yeast infection
- ⊕ If symptoms don’t improve with over-the-counter treatment
- ⊕ If you have recurrent infections (4 or more in a year)
- ⊕ If you’re pregnant
- ⊕ If you have other health conditions, like diabetes or HIV
The Impact of Yeast Infections
While not typically dangerous, yeast infections can significantly impact quality of life. They can cause discomfort, interfere with sexual activity, and even lead to emotional distress. It’s crucial to address them promptly and effectively.
Yeast Infections in Men
While less common, men can also get yeast infections. These typically affect the penis. Yeast infections in men can cause:
- ⊕ Redness and irritation on the penis
- ⊕ A burning sensation
- ⊕ A rash
- ⊕ Discharge under the foreskin
Men with diabetes or weakened immune systems are at higher risk. Treatment usually involves antifungal creams or oral medications. The fungus Candida albicans can also cause infection in men.
Yeast Infections and Sexual Health
It’s important to note that while yeast infections can be uncomfortable, they’re not considered sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, sexual activity can sometimes lead to yeast infections or make existing infections worse.
If you have a yeast infection, it’s best to avoid sexual activity until the infection clears up. If you do have sex, use protection to prevent passing the infection to your partner. Having unprotected sex can increase your chances of getting a transmitted infection.
FAQ
While mild yeast infections may occasionally resolve on their own, most require treatment. Without proper care, symptoms can persist or worsen, causing discomfort and potentially leading to complications. It’s best to seek treatment at the first sign of yeast infection symptoms.
Several conditions can mimic yeast infection symptoms, including bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, and certain sexually transmitted infections. Allergic reactions to feminine hygiene products or even certain skin conditions can also cause similar discomfort. This is why it’s crucial to get an accurate diagnosis from a healthcare provider.
Yeast infections are typically caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans. This can happen due to factors like antibiotic use, hormonal changes, a weakened immune system, or high blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. Lifestyle factors such as wearing tight, non-breathable clothing or using scented feminine products can also contribute.
Common symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection include intense itching, burning, and irritation in the vaginal area, along with a thick, white, odorless discharge. Other signs can include redness and swelling of the vulva, pain during urination or intercourse, and a rash. However, it’s important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it’s best to get a proper diagnosis from a healthcare provider. If you develop symptoms, you should contact your healthcare provider.
While some symptoms overlap, yeast infections typically don’t cause pain during urination or a strong odor, which are more common with certain STDs. The best way to differentiate is through proper testing. If you’re unsure, especially if you’ve had unprotected sex recently, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
Understanding what a yeast infection is and how it affects your body is the first step in effectively managing this common condition. While these infections can be uncomfortable and disruptive, they’re usually easily treatable with the right approach. Remember, if you’re experiencing persistent or recurrent symptoms, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider. They can provide a definitive diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific situation. By staying informed and proactive, you can effectively manage yeast infections and maintain your overall health and well-being.