Mid-winter is upon us, and the familiar chorus of coughs and sneezes fills the air. Wondering if it’s too late to defend yourself with a flu shot?
Fear not—health experts confirm that no matter how deep into flu season we are, vaccination remains your best defense against the virus. Securing a flu shot later in the season can still offer significant protection, even if the flu has already made its presence felt in your community. Ideally, vaccinations should be administered in early fall, around September or October, before flu activity peaks. However, receiving a flu shot at any point during the season is preferable to skipping it entirely.
Flu seasons can vary, typically peaking between December and February, but activity can start as early as October and extend into late spring, concluding around May. Opting to get vaccinated mid-season can still shield you from late-surging strains of the virus, ensuring your health remains guarded as the season progresses.
Remember, it’s never too late to take action. Get your flu vaccination today at NextCare and stay protected against the flu. Better safe than sorry!
NextCare is one of the nation’s largest providers of urgent care and occupational medical services. With 170+ clinics in Arizona, Colorado, Kansas, Michigan, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Texas, Virginia and Wyoming, we offer exceptional, affordable care to patients across the country.
Who Should Get Vaccinated? Understanding Target Demographics
Flu vaccination is essential for everyone, especially for those at higher risk of flu complications. These key groups include:
- ⊕ Seniors (65 and older): More susceptible to severe flu complications, seniors are advised to get a high-dose or adjuvanted flu vaccine for better protection.
- ⊕ Young Children (6 months to 5 years): Children in this age group are at higher risk of severe flu symptoms and complications.
- ⊕ Pregnant Women: Flu shots are safe during pregnancy and protect both the mother and the unborn child from severe flu complications.
- ⊕ Individuals with Chronic Health Conditions: Those with conditions such as asthma, diabetes, and heart disease are more likely to suffer from severe flu-related issues.
Vaccinating these groups not only protects them but also helps reduce the spread of the flu virus in the community.
Understanding the Different Types of Flu Vaccines
When considering a flu vaccination, it’s important to know the options available to you. Each type of vaccine is designed to protect against the flu, but they differ slightly in their formulation and who they are recommended for.
- ⊕ Inactivated Flu Vaccines (IIVs): The most common type of flu shot, these vaccines contain killed virus and are given by injection. IIVs are approved for use in people 6 months of age and older, including healthy individuals and those with chronic health conditions.
- ⊕ Recombinant Flu Vaccines: These are a newer type of flu vaccine that do not use flu viruses grown in eggs. This makes them a good choice for those with egg allergies. Recombinant vaccines are suitable for adults 18 years and older.
- ⊕ Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine (LAIV): Also known as the nasal spray flu vaccine, LAIV is made with live, weakened flu viruses that do not cause illness. It is approved for use in non-pregnant individuals, 2 through 49 years of age who do not have underlying health conditions.
- ⊕ High-Dose Flu Vaccine: Specifically designed for people 65 years and older, this vaccine includes four times the antigen of standard flu shots, offering better protection for the aging immune system.
- ⊕ Adjuvanted Flu Vaccine: This vaccine contains an additive that creates a stronger immune response. It is also targeted at older adults, who may benefit from an enhanced vaccine.
Each of these vaccines is targeted to meet different needs based on age, health conditions, and potential allergies. Choosing the right vaccine can enhance your protection against the flu. Always consult with your healthcare provider to select the vaccine that best suits your individual health needs.
By staying informed about the different types of flu vaccines, you can make a well-informed decision to protect yourself during the flu season. Get vaccinated today to reduce your risk of flu complications and help maintain your health and vitality.
Safety Record and Side Effects of Flu Vaccines
Concerns about flu vaccine safety and side effects are common, but evidence supports the safety and efficacy of flu vaccines:
- ⊕ Safety Record: Flu vaccines have a good safety record. Hundreds of millions of Americans have safely received flu vaccines over the past 50 years, and extensive research supports their safety.
- ⊕ Common Side Effects: Typical side effects are mild and short-lived, including soreness at the injection site, low-grade fever, and mild aches.
- ⊕ Severe Reactions: Severe allergic reactions are extremely rare. The CDC and FDA closely monitor vaccine safety, ensuring the risks remain much lower than the potential complications from the flu itself.
Avoiding Flu Complications
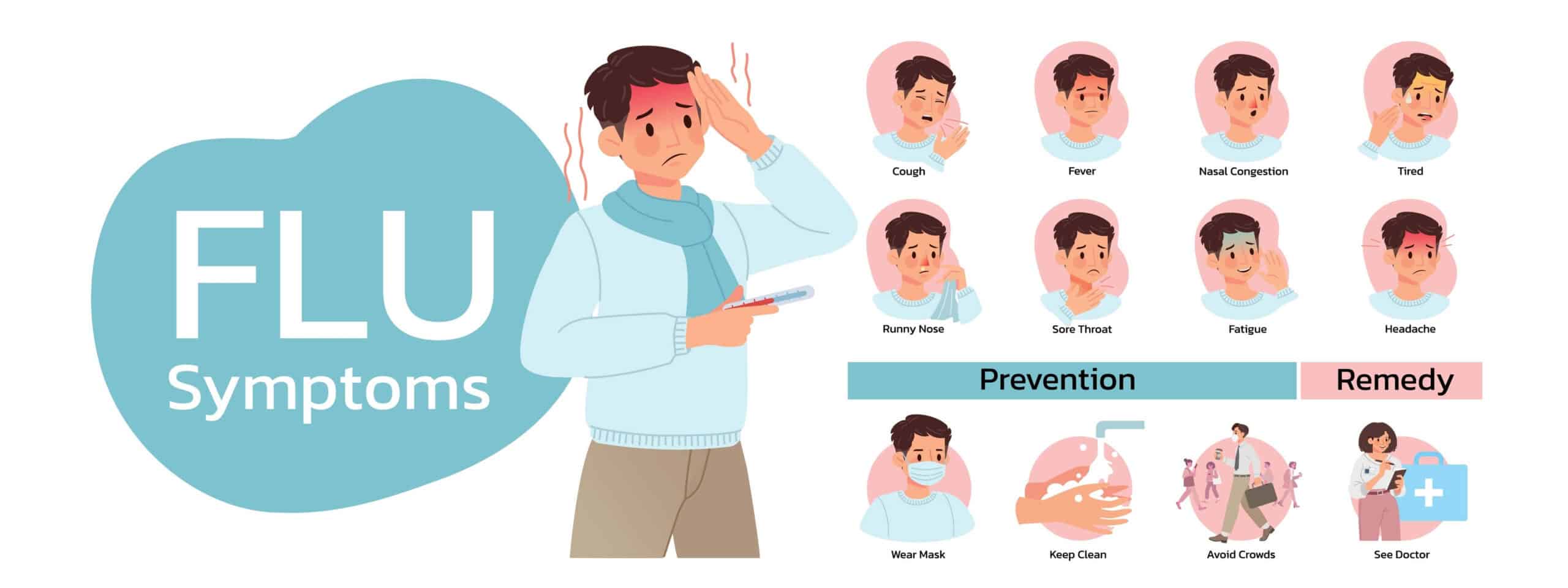
This flu season is expected to be more severe than in years past for older individuals. Unfortunately, the strains of flu virus that this year’s vaccine protects against aren’t a good match for the most common strain of the flu circulating this year, largely because the virus itself has mutated, according to the CDC.
This means that in addition to getting vaccinated, which can still offer some protection against the flu, you might also want to consider paying a visit to your doctor if you have a high persistent fever or can’t shake the flu. He or she can prescribe an antiviral medication that may help your body kick the flu more effectively. Seeing your doctor is even more important if you have a condition that puts you at higher risk for flu complications.
Typical symptoms of the flu to watch out for include:
- ⊕ Fever
- ⊕ Nasal congestion
- ⊕ Chills
- ⊕ Body aches
- ⊕ Fatigue
As you consider getting your flu vaccination, it’s also important to recognize the symptoms that differentiate the flu from other respiratory illnesses. With similar symptoms overlapping among the flu, colds, and COVID-19, understanding these distinctions can help you seek the appropriate treatment and preventive measures. For a detailed comparison and expert guidance, read about the key differences between COVID-19, the flu, and a cold.
Learn more about what types & virus strains that are in this years flu shots —>
FAQs About Flu Vaccination
No, flu shots cannot cause flu illness. The viruses in the flu shot are inactivated (killed), which means they cannot cause infection.
The best time to get vaccinated is before flu viruses begin spreading in your community, ideally by the end of October. However, getting vaccinated later can still be beneficial.
Flu vaccines are formulated each year to match the strains predicted to be most common. While effectiveness can vary, recent studies show that flu vaccination reduces the risk of flu illness by between 40% and 60% among the overall population.
A flu vaccine can reduce flu illnesses, doctors’ visits, missed work and school due to flu, as well as prevent flu-related hospitalizations.
Yes, the CDC recommends that everyone 6 months of age and older should get a flu vaccine every season with rare exceptions.
The flu vaccine provides protection throughout the current flu season, which typically spans from fall to spring. Its effectiveness can diminish over time, so an annual vaccination is recommended each fall to ensure optimal protection against the evolving strains of the flu virus.
After receiving a flu shot, you should avoid strenuous physical activities and excessive alcohol consumption for 24 hours to allow your body to respond properly to the vaccine. It’s also wise to stay hydrated and monitor the injection site for any unusual reactions.
The side effects of this year’s flu shot are generally mild and similar to those in previous years. They may include soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site, low-grade fever, and mild aches. These symptoms are temporary and usually resolve without treatment within a few days.
While it’s not necessary for everyone to rest after receiving a flu vaccine, if you feel tired or unwell, taking it easy can help your body recover and respond to the vaccine. Listening to your body and resting if needed is beneficial.
